What is Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgery?
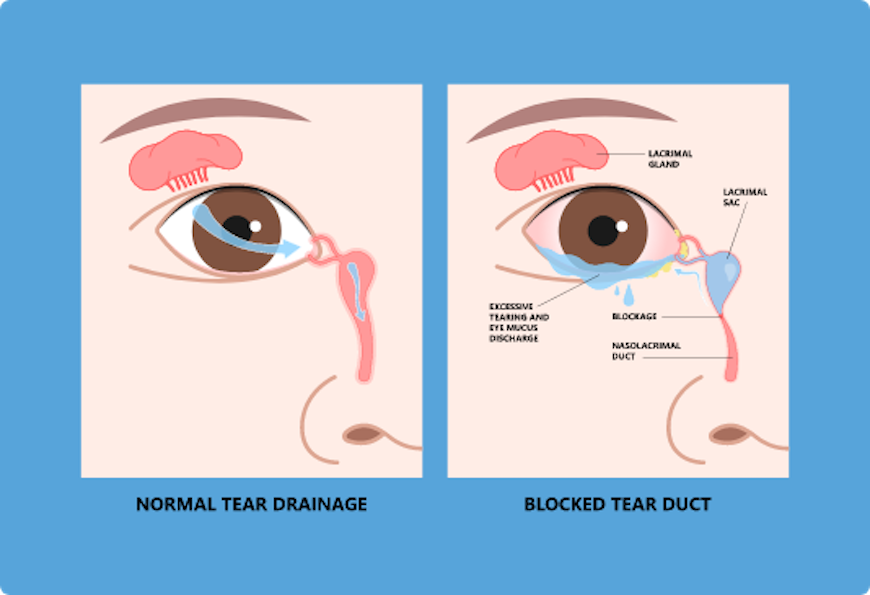
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgery is a procedure that aims to eliminate fluid and mucus retention within the lacrimal sac, and to increase tear drainage for relief of epiphora (water running down the face). Nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) can result in a watery eye, due to obstruction of the outflow of tears.

Procedure
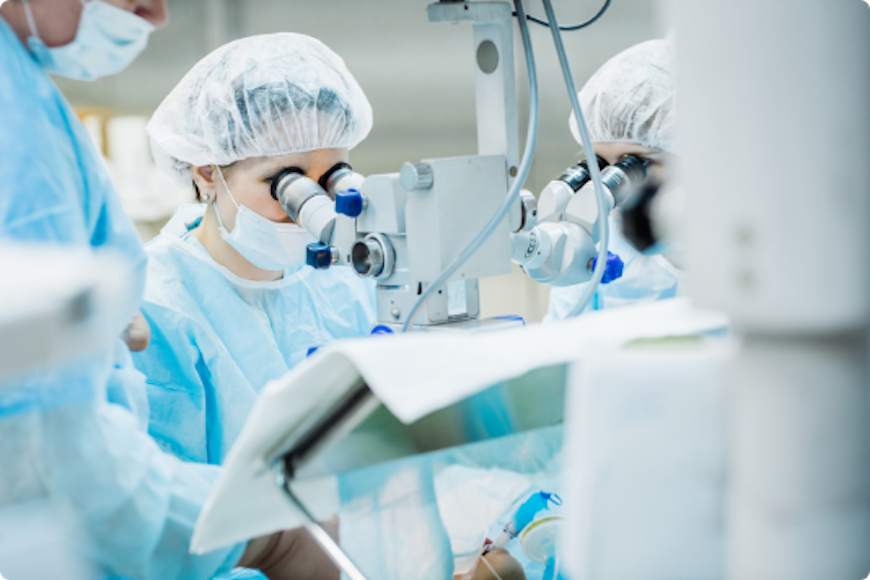
Surgery is often performed under general anesthesia, but may be performed under local anesthesia according to patient or surgeon preference. DCR can be achieved from an external (through a facial incision) approach or from an endoscopic (using a small telescope and instruments through the nose) approach. The goal of the procedure is to bypass the obstructed nasolacrimal duct and allow for tear drainage into the nose directly from the lacrimal sac. External DCR approaches the lacrimal sac through a small incision between the eye and the nose. The lacrimal sac is identified and opened into the nasal cavity. To maintain the opening, the surgeon may use sutures or stents. Endoscopic DCR accomplishes the same goal, but is performed through the nose with the use of telescopes and small instruments. This approach to DCR is now commonly performed because it avoids a facial scar, and is generally associated with less pain.
What are the risks?
In the endoscopic approach, pain is minimal and can be controlled with pain medications. Infection is uncommon and bleeding should be minimal, but rarely can be significant. Scarring within the nose may occur, leading to blockage of the opening and recurrence of tearing. Although extremely rare, the major risk of the procedure is bleeding within the orbital cavity (orbital hematoma) or injury to an eye muscle, which may cause double vision or vision loss. Scar and temporary bruising will occur with external procedures, although these should be relatively minor. If your surgeon prefers to keep a stent in place afterwards, prolapse (movement out of the nose or up into the eye) may occur, which requires stent adjustment or removal.

Outcome
DCR is a fairly simple outpatient procedure. Overall success rates exceed 90%, although in particular cases the likelihood of success may be lower. The risks and side effects of the procedure are relatively low, and can potentially lead to a long-lasting relief of bothersome tearing.

